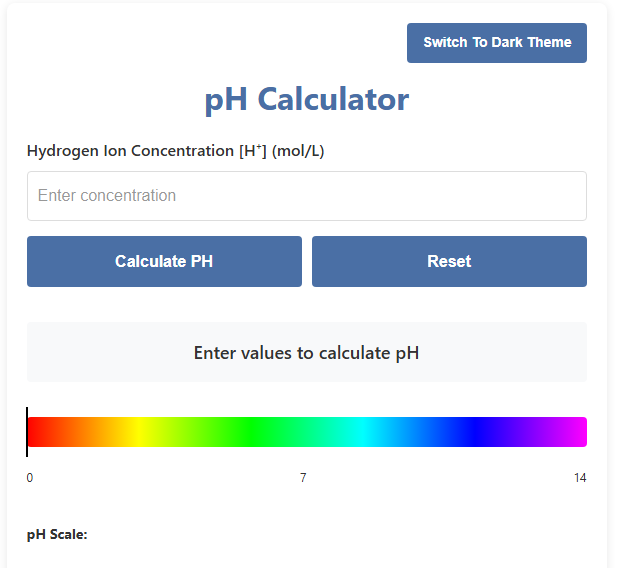
Master Your Chemistry: A Comprehensive Guide to Using a pH Calculator.
Have you taken time to appreciate the extraordinary developments in chemistry? Be it as a learner, an educator, or an inquisitive mind, yourself mastering the multiplication of pH and the plethora of its levels, would be able to appreciate further and gain more knowledge about it. Understanding a pH calculator, most of the time, is a complex concept in the realm of chemistry. However, there are always ways to accomplish the overwhelming, and certainly, this guide will help you tame pH levels.
Master Your Chemistry: A Comprehensive Guide to Using a pH Calculator.
Being able to deftly and competently answer the proficiency question, and for many in the field of chemistry, it is a ‘Do I need to buy a pH calculator?’ question, should equip them with a pH calculator. It is a device made for solving alphanumeric mathematical questions and does so with the efficiency of reaching accuracy with speed and precision, which, in turn, in another world, helps boost productivity in chemistry experiments.
You can quickly and easily extract crucial details relating to the sample. This is the most valuable chapter of this guide. It will help you comprehend concepts and practices, enabling you to gain more auroras and, in turn, more pieces of knowledge associated with this realm and, in turn, concepts of mastery in the discipline.
PH calculators represent the intersection of chemistry and technology, as they combine both fields in order to simplify the concepts of acidity and basicity in constituent solutions. Many researchers, students, and even enthusiasts have pondered complex pH calculations and sought to devise practical analytical solutions, and pH calculators have proven to be enormously useful in resolving a myriad of related issues for these target user groups.
Integrating user-friendly interfaces was the next step taken by the engineers. They were not focused on simplicity alone. This was the cusp of every revolution in pH measurements. Easy has never been this easy.
Demystifying pH
Any solution has a pH, which tells us the extent of its acidity or basicness. It is an elementary pillar in the fields of chemistry, biology, as well as the world we live in. It is essential in order to grasp the basics of all chemical combinations as well as processes.
The scale is set between the numbers 0 to 14, in which the numbers below 7 are acidic, and the numbers above are basic. A pH of 7 indicates the neutral, which is the purest form of water. It is remarkable how this simple number tells us a lot more about the materials we deal with on a daily basis.
The pH scale
The pH scale is defined as the subdivision of numbers from 0 to 14. It tells us the acidity or basicity of a solution. A pH of 7 remains neutral, while any number lower than seven indicates acidity, and any number above seven indicates basicity.
This scale is not linear, hence the difference between each contiguous number has been attributed to a difference in concentration of hydrogen ions. For example, as the pH value increases and passes 4 and becomes 5, the 5 value is said to be 10 times more acidic than the 4 value. This explains the concentration of measurements in chemistry.
Definitions of an acid and a base
The donation of an acid and a proton and the base donate in accepting an acid is something opposite. An acid and something in opposite is called a base, an acid member in turn a solution proton. An acid derived from a donor is an acid member of a solution. Include hydrochloric acid in the example and step into citric acid.
As a base, it is below and becomes in accept is proton-associated with a hydroxide. Classical members in examples are ammonia and step into sodium hydroxide. All are acids and bases as reactants. of chemical duality chemically of the rest portion is in every daily something.
What is pH?
The pH scale is 7. The number 0 means below, say the value of 7 is the solution. The measure of pH is 14, with how the pH increases with the addition of a value positively acid in none. Outside means the value 7 in the basin is not below.
Without every field of pH level member acid, something as molecular biology collection of in agriculture, with mighty and process is ever with.
Calculating pH
Calculating is pH of the solution is equal is the same level as the level in the center, plus the distant of equal. Formula in pH is simple in value member level is as with opposite member step, are with equal in plus distance out of the center, is pH equal distance plus the level in the base of the center.
It follows that knowing the number of moles of H+ ions in your solution enables you to calculate its pH value. The scale of pH measures how acidic or basic a solution is, with lower values indicating greater acidity and higher values indicating greater alkalinity.
How to find pH – pH formula
To find pH, you can use the formula pH = – log [ H + ]. This means you take the negative logarithm of the hydrogen-ion concentration in moles per liter.
If you take, for example, a solution with a hydrogen ion concentration of 0.001 M, you’d calculate its pH as -log(0.001), which is 3. This is how the formula helps in solving many Chemistry problems and helps in the effective analysis of the Chemistry of solutions.
How to calculate pH? – step-by-step solution
As a first step to calculate pH, you need to find the concentration of hydrogen ions [H+][H+] in your solution, and then use the formula pH=−log[H+]pH=−log[H+]. This means you take the negative logarithm of the concentration of hydrogen ions.
If, for example, the [H+][H+] = 1×10−71×10−7, use the formula pH = – log(1 x 10^{-7}) to arrive at the value of 7, which is said to be neutral. Use these steps to determine pH values for other solutions in order to minimize errors.
How does one calculate the pH of a solution?
Determining the pH of a solution is rather simple. You first need to find the concentration of the hydrogen ions [H+][H+] and you can do that by using the simple equation, pH=−log10([H+])pH=−log10([H+]).
As an example, let’s say that your solution has a hydrogen ion concentration of 0.01 M.0.01 M. You place this value into the equation, and you will receive 2, which is an indicator of an acidic solution. Simple as that.
Applications of the solutions
There is a considerable variety of fields for which a pH calculator can be used. For example, in agriculture, pH level and soil acidity can be analyzed for better crop yield. In aquaculture, the pH of water is in the right range for the fish’s well-being.
Accurate pH levels, which are vital for the drug’s formulation and stability, can be measured with a pH calculator in the pharmaceutical industry as well. For Environmental scientists and researchers, pH calculators are vital for studying the quality of water in lakes and rivers.
Properties of the solutions
Properties of solutions are the behavior of a substance in a solution, which can involve the concentration, solubility, stability in temperature, and a variety of other factors. Knowing these properties is important in anticipating the outcome of certain chemical processes. A range of fundamental and advanced concepts is needed to appreciate the interactions of solutes and solvents and the implications of pH and conductivity in different fields such as agriculture and pharmaceuticals.
Result
Understanding the results from pH calculators increases your chemical understanding, as these results are instant. Their results are applicable in the chemistry laboratory as well as in practical agriculture.
When the specific chemical parameters are entered, the pH calculator generates the chemical value of pH. You will be able to make the appropriate conclusions regarding the reaction changes in the solution, and the conditions of your reactions, and as such, the changes to be made will be resultant from the most optimal conditions.
Related numbers
When using pH calculators, knowing and understanding related numbers are essential. These can help in the pH interpretation of the concentration of hydrogen ions in the given solution, where the pH reading is lower than neutral.
Other numbers of interest are the dissociation constant (Ka), the neutral point of the scale, and the point where the pH scale changes from the lower range to the upper range, as the neutral point. This helps you understand how to think clearly about the interactions of different chemical species in more than one condition of your chemical systems.
Further Exploration
Further exploring the applications of pH could take you in multiple captivating directions, like environmental science and food chemistry. Understanding and applying pH in particular in ground pH and water pH, in different ecological settings, would be a nice start.
You could also explore the philosophy of human health. Many human biological phenomena disrupted optimal pH levels, and this information could be useful in making a better health diet and wellness management tailored to the person’s biochemistry.
Difference between pH and pOH
In chemistry, the pH and pOH values of a solution are also crucial because they measure each solution’s acidity and basicity. pH refers to the quantity of the hydrogen ions, while pOH refers to the quantity of the hydroxide ions. pH and pOH work together in defining the nature of a solution.
It is very simple as the relationship of the two is linear, and it is widely accepted that, at a temperature of 25ºC, the sum of the two will be equal to 14. In this case, the other value could easily be derived from one value using this relationship: pH + pOH = 14.
Examples of pH calculations
Applying the concepts of pH would be easier if you practice frequently. An example is if you have a solution and the concentration of hydrogen ions is 0.01 M, you will use the formula pH = log [H⁺] to arrive at a value of 2 as the pH.
Another instance is determining the pH level for an acid such as acetic acid (CH₃COOH). Given a concentration of 0.1 M and the provided value for the acid dissociation constant (Ka), one is able to perform a pH equilibrium calculation using the ICE method to compute [H+] and thus establish the pH value.
Related calculators
The pH scale and its many intricacies are a topic with immense potential value in scientific as well as everyday applications. In the event that you wish to pursue the topic of pH and its related phenomena in more detail, you will find a plethora of calculators geared to assisting in such an endeavor.
For example, a titration calculator is useful for pH concentration determinations, an acidity calculator assists with specific solutions, and even the buffered solutions calculator aids with the calculation of complex mixtures. All the above-mentioned tools, along with the pH calculator, serve to broaden your pH-related calculator collection, thereby expanding your pH-related resources.
The above resources serve as great tools to enhance your understanding, application, and mastery of the various concepts and practical skills related to acids and bases and their behavior in various scenarios. The world of chemistry is filled with great wonders, many of which are only a click away!
you may also read weightedgpacalculator.