Mastering Data Estimation: A Comprehensive Guide to Using an Interpolation Calculator
The ability to analyze and break down data is an ability that almost every professional and individual possesses in one form or the other. The only difference is the extent to how complex the data in question is complex. In situations where some data is unavailable or you need to formulate predictions for a certain situation, data interpolation becomes an integral piece of the puzzle.
Consider how easy it could be to complete the missing data by using an interpolation calculator. The ease with which the calculator helps you fill in gaps is what sets it apart.
In an increasingly data-driven world, these estimates can be generated almost instantaneously and are reliable due to the logic and thresholds set in the system. The ability to pass through several phases of evaluations and still cope with the time restrictions makes these processes invaluable. The more you practice with these techniques, the easier it becomes to approach almost any data set with the confidence that you will master the complex problems and be able to arrive at sound conclusions.
Chapter 1: Data Estimation and Data Interpolation
Estimating data is to predict based on some available data points. Gaps are closed, and future points are predicted to estimate the data. It reconstructs the underlying data of complex numbers by converting raw numbers to actionable terms.
For more precise estimates, Interpolation fills the gaps. Making guesses about unknowns in a field of known data is what Interpolation concerns itself with. This technique adds more data points in order to assist in more precise decisions in complex fields like finance, engineering, and other hard sciences.
Why is Interpolation important in data analysis?
Estimating unknowns within known bounds is a problem of Interpolation, which assists the analyst in sifting through incomplete datasets.
Interpolation aids in closing the gaps in datasets. Relating data by making estimations based on known figures is important in how analysis is done. It strengthens insights and decisions based on actionable proposals rather than data that is guessed or assumed.
What are the various methods that can be used to do Interpolation?
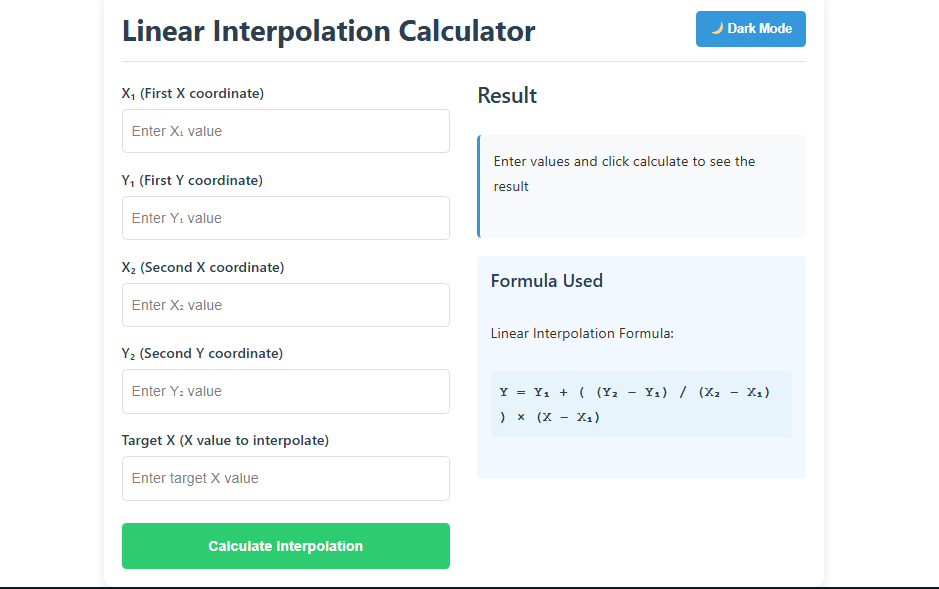
There are an endless number of methods for performing interpolations, and different data sets require different methods. The first and simplest would be the Linear Interpolation, which connects two points with straight lines. This is used whenever the world function’s output can be predicted.
Polynomial Interpolation fills the gaps of complex datasets by fitting higher-degree polynomials. More sophisticated than spline interpolation. Spline interpolation splits the range into contiguous sections and then ensures the sections are smoothly integrated. The nearest neighbor interpolation is the simplest form, which uses the closest known data and ignores everything else. Each of these techniques provides varied pros and cons depending on the type of data and the accuracy that is sought.
Linear Interpolation
Linear Interpolation is the most rudimentary method of approximation. It assumes the unknown value is on a straight line connecting the two known data points. It also assumes that the change between the two data points is uniform, and hence is are incremental calculation.
Linear Interpolation is commonly used across various domains like engineering and finance because there is not much time available, and the user is not concerned with accuracy. It is the type of analysis that can easily be carried out by collegians or a user who is in a hurry and does not want to solve complicated problems.
Polynomial Interpolation
Polynomial Interpolation is achieved when unknown data points are associated with a set of known points by using polynomials. It is able to associate the known points with a single polynomial in the form of the sine or the form of the cosine.’
One important consideration is the order of the polynomial within the model; higher order polynomials can capture dramatically more complex behaviors within the data, but in doing so, can also create unwanted and inaccurate oscillations between the data points. Therefore, attaining the right order is crucial for attaining desirable outcomes in your analysis.
Spline Interpolation
Spline interpolation is an important high-order interpolation technique that joins piecewise polynomials to construct a curve that passes through a given set of points. It is more sophisticated than a linear approach as it offers continuity to the function and its derivatives. Therefore, it is more useful in practical situations that demand a high level of accuracy.
Analysts can focus on more complex data sets that require meticulous attention to detail and smooth transitions throughout. The sleek curves that can be produced from splines can add important aesthetics to a functional piece of data, achieving a fine balance between accuracy and stylistic presentation.
Nearest Neighbor Interpolation
Nearest neighbor interpolation is the most basic approach to estimating data sets and can be accomplished by associating with an unknown point, the value of a known data point closest to it. This is a quick approach to data set estimation, therefore best suited to a situation where time is of the essence.
Even though this approach is efficient, it can yield inaccurate results. Because there are no opportunities to smooth out adjacent points, the values can be blocky or seemingly discontinuous.
Logarithmic Interpolation
Logarithmic Interpolation is used with datasets that grow or decrease exponentially. By taking logarithms of the values, it is possible to unwarp them, simplifying the estimation of absent values. This is, for example, desirable in areas of science and finance where there are exponential changes in values.
This approach is effective and balances precision with ease of calculation. Interpolation is accurate to the extent that the proportions of the underlying dataset are retained. Within the estimates, essential trends and values are preserved.
Newton Interpolation
Newton Interpolation is an efficient technique for estimating the value of discrete data points. It uses the idea of divided differences to make a polynomial that intersects with all of the points, which is particularly useful for scattered datasets.
The technique provides ease and accuracy when predicting unknown values. As new data streams in, the Interpolation can be modified without complete reconstruction. This ease of application makes Newton Interpolation vital in many branches of engineering and science.
Lagrange Interpolation
Lagrange interpolation is a powerful technique that formulates a polynomial to estimate unknown data points. It is highly advantageous when there is a need to form a polynomial that passes through and smoothens transitions to disorganized data points.
The technique uses the other form of the Lagrange formula, which generates a Lagrange basis polynomial system to determine the Interpolation of a given set of data points. Each point has a corresponding polynomial, which helps in crafting the final estimate and aids in the refinement of the final result. It has the most vital role to play in engineering, simulations, and scientific research, where precision is crucial.
How Interpolation Calculators Work
Given a set of data points, interpolation calculators compute missing values of a set of ranges that fall within the known points of the set. They use the boundary points to formulate a smooth and continuous curve that passes through and offers the best estimate.
Different methods of data processing provide different trusted estimates with their approximating calculations. This is helpful in easing the workload of complex estimations in the fields of engineering and statistics.
Estimation With the Help of an Interpolation Calculator
Estimation of data becomes easier with precise tools. This exposure gives the ability to work with definite values. This can then assist the users to make educated guesses about the variables that lie unknown. This is mainly beneficial in the fields of engineering, banking, and even in scientific terms.
With the help of these calculators, you can reduce the chances of error that comes with manual calculation. After spending a limited time on a few clicks, you can build more efficient approaches for your decisions with data that has been refined by analytics.
Common Rough Edges in Interpolation and the Best Approaches to Correct Them
Mistakes in Interpolation can stem from the use of inappropriate methods on the received data. For example, using linear Interpolation on nonlinear data will result in greatly erroneous outcomes. Always take time to evaluate how your data acts before selection.
Another disregard of the scope of the problem has closed off the conditions of the problem boundary. Misleading results may be produced by extrapolating beyond the known values. To avoid this, if it is feasible, avoid the range of discernible points. Focus on the area of available data and calculating estimates and conclusions from the analysis of the data. It is safer. Safe, reliable estimates and insights are vital, and an Interpolation calculator may provide these insights.
Benefits of the Interpolation Calculator
The calculator has capabilities that facilitate data interpolation. It reduces the time and the input of the individual. The results have a high level of accuracy, which eas difficult to achieve with large data sets and Excel spreadsheets.
The calculator allows the user to engage with the tool with ease and assumes that even entry-level employees with no experience with the tool can appreciate the ways in which it simplifies data. The diversity of analysis is great, and interpolation use is easy to engage with. It is an invaluable tool that simplifies problem types.
The use of Interpolation with data of a diverse nature.
The Interpolation system can be applied with ease. The Interpolation with the use of diverse data is invaluable. Use of diverse data spanning a range of fields.
Engineering is an invaluable area that uses Interpolation. It is used to estimate values within known data points to increase accuracy, which ensures a high level of manufacturing precision.
Within medicine, Interpolation helps to analyze records of patients and forecast associated outcomes of particular treatments. In a similar vein, meteorologists use Interpolation when estimating future weather patterns based on previous climate data. These cases exemplify how Interpolation improves processes across different sectors.
Manual Interpolation vs Using a Calculator – Pros and Cons
Manual Interpolation offers a better understanding and finesse over a particular process. It fosters ingenuity, especially on what equations to apply or which methods to employ. Nevertheless, the process can be tiresome and susceptible to mistakes.
In contrast, the use of an interpolation calculator greatly simplifies the estimation procedure. Calculators, while often providing inaccurate results, may also lack interpretative depth pertaining to the overall process. If users overestimate the automated processes, they may lack the understanding to analyze the principal concepts of the material.
Conclusion
The fundamentals of mastery over data estimation using Interpolation sculpt a more intricate dimension of analytical prowess. It is far more interesting to use an interpolation calculator to use an estimation in order to perform complex calculations on data so that meaningful insights can be derived. Understanding the different methods of estimation and their use cases, one is better poised to make an optimal choice in any situation.
Steer clear of most pitfalls by understanding possible oversights that may result in blunders in Interpolation. The use of electronic devices such as calculators not only enhances precision but also increases the efficiency of time utilization.
With the relentless progression of industries, the need for accurate information management increases. No matter if you are in finance, engineering, or any branch of scientific research, knowledge of these principles will guarantee that you remain ahead of the rest in this era dominated by data.
you may also read weightedgpacalculator.